Tunnel Segment Bolt Introduction
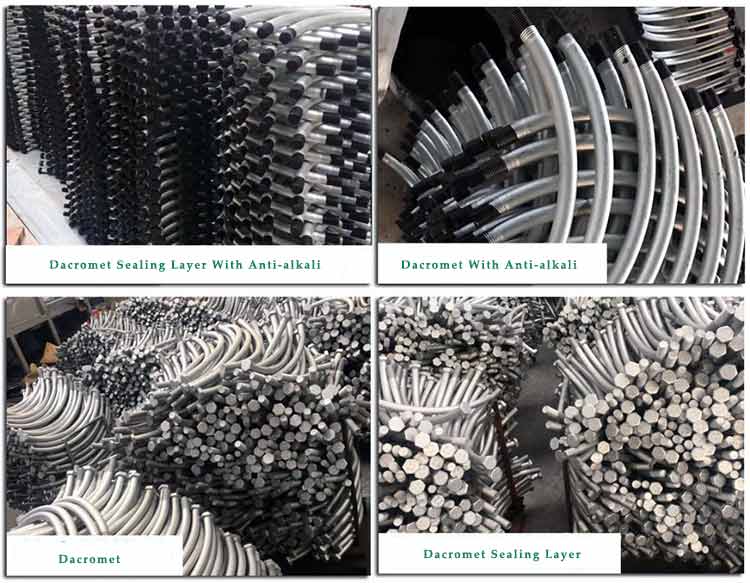
Shield segment bolts are special fasteners used to fasten or connect segments during the construction of shield tunneling machines. Several arched segments are connected by segment bolts to form a circle, and the entire tunnel surface is supported by this circle, so it is also called segment connector. Because it is specially used for shield tunnels, it is also called shield segment bolts or tunnel connectors. Shield machines are usually used in tunnel excavation. Tunnel transportation of soil and slag, and excavation and cutting of soil are inseparable from shield machines. Shield machines are usually composed of multiple segments, which are composed of pipes. Tunnel segment bolts are connected and tightened to form a cylindrical pipe, then the segment becomes the pipe wall, and the linear or arc-shaped fasteners are tunnel segment bolts. Tunnel segment bolts vary according to the shield diameter. Different sizes of segments have various designs and types. Tunnel segment bolts can also be called segment connectors. Commonly used surface treatments are: hot-dip galvanizing, sherardizing, dacromet, etc.



Shield Tunneling Method
The shield tunneling method is a construction method of digging tunnels under the ground. It has been widely used in Subway Line, railway, highway, municipal, hydropower and other tunnel projects. During the construction, in order to prevent the collapse of the soft foundation excavation surface or maintain the stability of the excavation surface when the shield machine is used for underground excavation, it is necessary to carry out lining operations in the tunnel at the same time, and lining prefabricated segments are reinforced with tunnel segment bolts. Due to the different pressures exerted on the shield by different geological conditions, the design mechanical properties of the shield segment bolts are more than 5.8, 6.8, 8.8, and 10.9.
Tunnel Segment Bolt Types
Usually tunnel segment bolts are divided into 6 types, namely: hexagonal head arc segment bolts, non-standard segment bolts, double-ended straight segment bolts, double-ended arc segment bolts, hexagonal flange face circle Arc thread segment bolts, hexagon head arc thread segment bolts. In addition, the segment connecting bolts can also be classified according to the stress. There are usually 3 grades, namely: 5.8 machine (material is Q235), 6.8 (material is 45#), 8.8 (material is 40Cr) ), in which the surface treatment is galvanized.
 Arc Hex Head Joint Bolt
Arc Hex Head Joint Bolt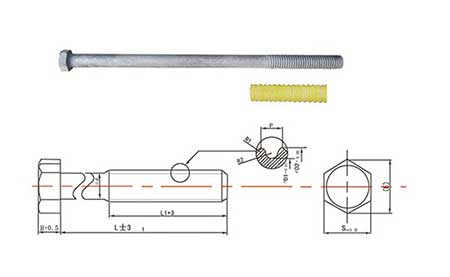 Arc Hex Head Joint Bolt Round Thread
Arc Hex Head Joint Bolt Round Thread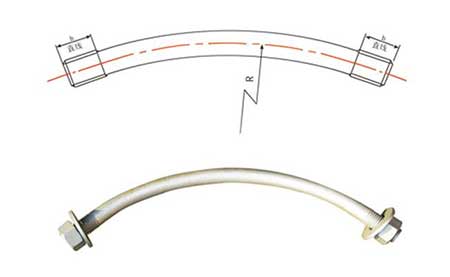 Arc Stud Joint Bolt
Arc Stud Joint BoltThe tunnel segment bolts can assemble several segments together. Some of the segments have a certain arc, and some are straight. The connection and fastening between segments depends on the action of segment connection bolts. The application range of segment connection bolts It is widely used in building segment connection, shallow buried longitudinal segment bolt, Subway Line shield, Subway Line segment connection, tunnel segment connection and other projects.

| Dimension | Arc Length mm | Tensile Strength | Surface Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| M25~M39 | 480~880 | 4.6、4.8、5.6、5.8、8.8 | Dacromet, Hot dip Galvanized |

| Dimension | Arc Length mm | Tensile Strength | Surface Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| M25~M48 | 480~880 | 4.6、4.8、5.6、5.8、8.8 | Dacromet, Hot dip Galvanized |
Subway Line Tunnel Shield Bolt Application
Subway Line Tunnel shield bolts are not a special kind of bolts, but a general term for certain types of bolts that are often used in Subway Line construction. Subway Line tunnel shield bolts are characterized by high anti-corrosion standards, good steel performance, and curved and straight shapes. The bolts used to repair Subway Line cement structures are called Subway Line bolts. They are widely used in mines and Subway Line projects. Subway Line bolts include longitudinal and circumferential Subway Line bolts. In some projects, longitudinal and circumferential Subway Line Tunnel bolts are the same specification. In some projects, the longitudinal and circumferential Subway Line bolts are of two different specifications with different strength levels.
| Dimension | R | B | Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| M30X610 | 380 | 45 | Shanghai Subway Line |
| M30X617 | 360 | 42 | Suzhou Subway Line |
| M30X620 | 360 | 42 | Hangzhou Subway Line |
| M30X617 | 360 | 42 | NanJing Subway Line |
| M30X627 | 360 | 42 | NanJing Subway Line |
| M30X617 | 360 | 42 | Wuxi Subway Line |
| Dimension | R | Arc Length | B | Project |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24X531 | 350 | 476 | 55 | BeiJing Subway Line 7 |
| 24X531 | 350 | 476 | 55 | BeiJing Subway Line 6 |
| 24X521 | 350 | 471 | S0 | BeiJing Subway Line 10 |
| 24X523 | 350 | 473 | 50 | NanJing Subway Line 2 |
| 24X516 | 3S0 | 463 | 50 | Shenyang Subway Line 2 |
| 24X505 | 350 | 460 | 45 | Shenyang Subway Line 1 |
| 27X518 | 350 | 473 | 45 | Zhengzhou SubwayLine |
| 27X518 | 350 | 473 | 45 | Changsha Subway Line 1 |
| 27X518 | 350 | 473 | 45 | Wuhan Subway Line 2 |
| 27X540 | 380 | 497.5 | 42 | Xian Subway Line 2 |
| Dimension | R | B | Mechanical Property | Project |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M30X606 | 436 | 170 | 8.8 | BeiJing South-to-north water diversion Tunnel |
| M36X667 | 489 | 180 | 8.8 | BeiJing South-to-north water diversion Tunnel |
| M30X606 | 436 | 170 | 8.8 | First underground railway tunnel |
| M36X667 | 489 | 180 | 8.8 | First underground railway tunnel |
Subway Line tunnel segment bolts are used in many projects and are a common fastener. However, due to the working environment, rust and corrosion are prone to occur during use. Corrosion of Subway Line segment bolts not only affects the appearance of Subway Line segment bolts, but also affects the mechanical property, such as the mechanical properties and tensile strength of Subway Line segment bolts will be reduced, so that the service life of the segments and Subway Line segment bolts will be reduced. This will not only increase the cost of the enterprise, but also increase the difficulty of subsequent maintenance work. Therefore, when using Subway Line tunnel segment bolts, attention must be paid to the anti-corrosion treatment.

Subway Line tunnel bolts are mainly used in Subway Line construction projects, mainly assembling segments together to form pipes. They work in a humid environment, so in order to prolong its service life, we need to do anti-corrosion treatment. Before the tunnel shield bolts are used, some inspection work should be done to observe whether the shape and size of the Subway Line tunnel bolts are abnormal, the arc of the rod is normally bent, and whether the tensile load is normal.
Mechanical Property of Subway Line Tunnel Segment Bolt
| Mechanical and Physical Properties | Performance Level | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.6 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 8.8 | ||||
| d≤163) | d>163) | |||||||||
| Nominal Tensile Strength | N/mm2 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 800 | |||
| Minimum tensile strength | N/mm2 | 330 | 400 | 420 | 500 | 520 | 600 | 800 | 830 | |
| Vickers hardness HV F≥98N | min | 95 | 120 | 130 | 155 | 160 | 190 | 250 | 255 | |
| max | 2206) | 250 | 320 | 335 | ||||||
| Brinell hardness HB F=30 D2 | min | 90 | 114 | 124 | 147 | 152 | 181 | 238 | 242 | |
| max | 2096) | 238 | 304 | 318 | ||||||
| Rockwell hardness HR | min | HRB | 52 | 67 | 71 | 79 | 82 | 89 | / | / |
| HRC | / | / | / | / | / | / | 22 | 23 | ||
| max | HRB | 95.06) | 99.5 | / | / | |||||
| HRC | / | 32 | 34 | |||||||
| Surface hardness HV 0.3 max | / | 7) | ||||||||
| Yield point N/mm2 | Nominal | 180 | 240 | 320 | 300 | 400 | 480 | / | / | |
| min | 190 | 240 | 340 | 300 | 420 | 180 | / | / | ||
| Specified non-proportional elongation stress N/mm2 | Nominal | / | / | 640 | 640 | |||||
| min | / | / | 640 | 660 | ||||||
| Guaranteed stress N/mm2 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | ||
| 180 | 225 | 310 | 280 | 380 | 440 | 580 | 600 | |||
| Breaking torque MB,N.m min | / | according to GB/T3098.13 regulations | ||||||||
| Elongation after breaking % min | 25 | 22 | / | 20 | / | / | 12 | 12 | ||
| rate of reduction in area % min | / | 52 | ||||||||
| Shock absorption work Aku,min | 25 | 30 | 30 | |||||||
| Head firmness | No break | |||||||||
| Minimum height of undecarburized thread E | / | 1/2H1 | ||||||||
| Maximum depth of fully decarburized layer G,mm | / | 0.015 | ||||||||
| Hardness after tempering | / | The difference between the average hardness before and after tempering is not more than 20HV | ||||||||
| Surface defects | According to GB/T 5779.1 or GB/T 5779.3 regulations | |||||||||
Surface Treatment of Tunnel Segment Bolt




