Types of galvanized Steel Sheets - how are oiling, passivation, sealing, and phosphating combined?

The galvanized steel sheet is used to prevent corrosion of the surface of the steel sheet and prolong its service life. The surface of the steel sheet is coated with a layer of metal zinc. This zinc-coated steel sheet is called a galvanized sheet. Zinc plating is a cost-effective and effective method of preserving corrosion, and about half of the world's zinc production is used in this process.
Divided into 2 Major Types according to Production Methods
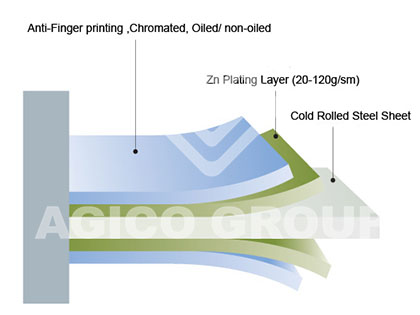
- Electrogalvanized sheet: A galvanized sheet produced by causing zinc ions to pass electrons through an electrolyte containing zinc ions to generate electrons to form zinc deposited on the surface of the strip.
- Hot-dip galvanized sheet: A galvanized sheet produced by galvanizing a cold-rolled or hot-rolled steel strip into a molten zinc bath on a continuous hot-dip galvanizing line.
The heat zinc coated steel sheet can be further divided into:
- Hot-dip pure zinc plate: The zinc content in the molten zinc solution is greater than 99%.
- Hot-dip galvanized iron alloy plate: The zinc content in the molten zinc solution is greater than 99%. Thereafter, a zinc-iron alloy layer is formed on the entire plating layer by an alloying treatment process, and the iron content in the alloy plating layer is usually 7 to 15%.
- Hot-dip aluminum-zinc plate: The content of aluminum in the molten zinc solution is about 55%, the content of silicon is about 1.6%, and the rest is zinc.
According to Surface treatment
The surface treatment of galvanized sheets is also sequential. It is not a random combination process. Different surface treatment processes have different uses. The following are some common surface treatment process combinations and their uses:
For example: The substrate is electrogalvanized plate
| Base Plate | layer 1 | layer 2 | layer 3 | Main Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric- Galvanized Steel Sheet | oil | Form a protection layer on steel sheet surface, reduce corrosion and scratch | ||
| Phosphating | Form dense fine phosphating film on steel surface to reduce corrosion. | |||
| Phosphating | oil | Reduce white rust and improve the molding performance | ||
| Phosphating | Chrome-free closure | Lubrication and enhance its anti-corrosion ability, reduce white rust, ready for paint. | ||
| Phosphating | Chrome-free closure | oil | Reduce white rust and improve the molding performance | |
| Chrome-free passivation | Applying an organic solution with no hexavalent chromium to produce a passivation film | |||
| Chrome-free passivation | oil | Reduce white rust on steel surface | ||
| Chrome-free no fingerprint | No fingerprint would show on steel surface with the special protection layer | |||
| Chrome free self-lubricating | It can improve the lubrication of steel surface |


